Pharmaceutical Engineering
cGMP for Engineers
cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practice) knowledge is crucial for engineers in the pharmaceutical industryto ensure quality of product. We provide training to engineers to make them understand about implementation of engineering activities impacting patient safety. Following are the key areas where engineers will get improved understanding
- Regulatory compliance: Ensures engineers design and maintain processes that meet strict regulatory requirements.
- Quality assurance: Helps in developing systems that consistently produce high-quality, safe pharmaceuticals.
- Risk management: Enables engineers to identify and mitigate potential risks in manufacturing processes.
- Process design: Guides the creation of manufacturing processes that inherently support cGMP principles.
- Equipment selection: Informs choices about appropriate, compliant manufacturing equipment.
- Validation: Assists in designing and executing effective validation protocols for processes and equipment.
- Documentation: Helps engineers create and maintain the extensive documentation required in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Contamination control: Crucial for designing facilities and processes that prevent product contamination.
- Troubleshooting: Aids in identifying and resolving issues in a compliant manner.
- Continuous improvement: Provides a framework for ongoing enhancement of manufacturing processes.

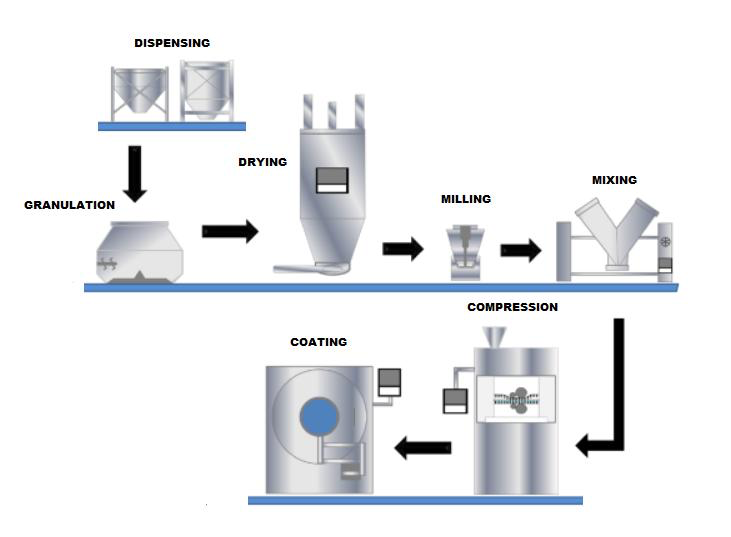
Unit operation review in cGMP framework
A unit operation review is a systematic evaluation of individual manufacturing steps or processes (unit operations) to ensure they comply with cGMP standards and consistently produce high-quality pharmaceutical products.
We review unit operations considering following key aspects:
- Process understanding: Thorough analysis of each step in the manufacturing process
- Risk assessment: Identifying potential points of failure or quality risks in each unit operation
- Control strategies: Implementing measures to mitigate identified risks and ensure consistent quality
- Documentation: Verifying records of processes
- Equipment qualification: Verifying if the qualification is appropriately executed
- Personnel training: Verifying that operators are adequately trained for their specific roles
- In-process controls: Establishing appropriate checks during the manufacturing process
- Validation: Confirming that the unit operation consistently produces expected results
- Continuous improvement: Identifying opportunities to enhance efficiency and quality
- Compliance with regulations: Ensuring alignment with relevant cGMP guidelines and regulatory requirements